Busca información sobre estos materiales y da ejemplos prácticos sobre en que se utizan dada su propiedad para transmitir o aislar del calor. También investiga si se dilatan por el calor.
Aluminio, corcho, goma, porcelana, lana, cobre, madera, cemento, arcilla y el hierro..
domingo, 31 de marzo de 2019
The materials properties
Pulsa este enlace.
Dilatation of alluminiums://www.youtube.com/watch?v=EWN_-mC9cPI
Dilatation of ironhttps://fq-experimentos.blogspot.com/2010/07/129-dilatacion-de-los-metales.html
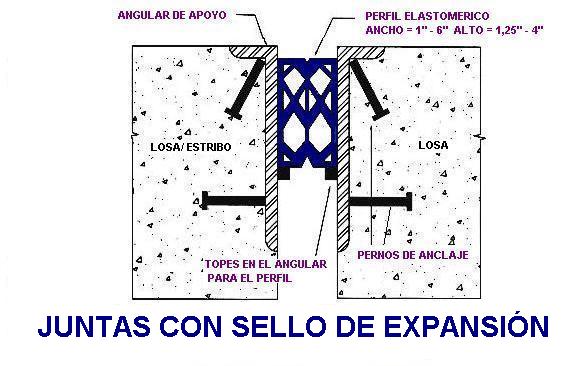
What problems can have the dilatation of materials in the bridges and the railways?


Dilatation of alluminiums://www.youtube.com/watch?v=EWN_-mC9cPI
Dilatation of ironhttps://fq-experimentos.blogspot.com/2010/07/129-dilatacion-de-los-metales.html
What problems can have the dilatation of materials in the bridges and the railways?



miércoles, 27 de marzo de 2019
domingo, 24 de marzo de 2019
Concurso de cuentos
Con motivo del día del Libro, El AMPA va a organizar un concurso de cuentos. Vosotros ya lo tenéis hecho, asi que solo falta que la presentación sea buena. Durante esta semana espero que los entregueis.
miércoles, 20 de marzo de 2019
Foto de la orla: 4 de Abril.
Ya tenemos cita para realizar la foto de la orla, que será el jueves día 4 de abril. Luis, el fotógrafo, nos mantiene el precio del año pasado (14 euros por alumno)
Lo que suele hacerse es que los alumnos llevan todos puesto un jersey o camiseta de color blanco liso.
Lo que suele hacerse es que los alumnos llevan todos puesto un jersey o camiseta de color blanco liso.
martes, 19 de marzo de 2019
Physical changes
Physical changes
Water going from a solid to a liquid: Melting
Water going from a liquid to a gas: Evaporation
Water going from a solid to a gas: Sublimation
Water going from a liquid to a solid: Freezing
Water going from a gas to a liquid: Condensation
Water going from a gas to a solid: Deposition
Water going from a liquid to a gas: Evaporation
Water going from a solid to a gas: Sublimation
Water going from a liquid to a solid: Freezing
Water going from a gas to a liquid: Condensation
Water going from a gas to a solid: Deposition
domingo, 10 de marzo de 2019
Basics on buoyancy
://www.pbs.org/wgbh/nova/lasalle/buoybasics.html

Density, mass and volume
Scientists use “density” to describe how much mass an object packs into a certain volume. Objects with high density have lots of material packed into a small space. Density determines something’s ability to float or sink. If an object has greater density than the liquid it is in, it will sink. If its density is lower than the liquid, it should float
4. Problem: A block of aluminum occupies a volume of 15.0 mL and weighs 40.5 g.
What is its density?
Mass is the amount of matter in an object or substance. It is measured in grams (expressed as g) and kilograms (expressed as kg). We typically use a balance to measure mass, but we can also find mass by measuring the Earth weight of an object with a weight scale. Then, scientists can calculate the mass by applying a complex formula that divides the weight by the force of gravity.
Volume is the amount of space that an object occupies.
Determining Volume with Water Displacement: Volume is a measure of the amount of space an object takes up. When an object is submerged in water, it pushes water out of the way. If you measure the amount the water level increases, you can find the volume of the water pushed out of the way which equals the volume of the object placed in the water. See the image below.
Final Volume (Water) - Initial Volume (Water) = Water Displaced = Volume of object

To determine the density of an unknown object, water displacement can be used to determine the volume of the object. You would measure the mass of the object using a balance.
Mass is usually measured to two decimal places, volume to one decimal place.
Ex. If we wished to determine the mass of the metal in the above image, let's say we determined its mass on the balance to be 4.40 grams.
| Lab Measurements | |
| Mass of object (g) | 4.80 g |
| Initial volume of water (ml) | 7.0 ml |
| Final volume of water (ml) | 9.0 mL |
| Water displaced (ml) | 2.0 mL |
| Volume of unknown metal (ml) | 2.0 cm3 |
* Remember mL = cm3 in volume measurement
- Calculate the density: Density = Mass / Volume = 4.80 grams / 2.0 cm3 = 2.4 g/cm3
- You would then identify the substance by looking at the density tables for substances to see what is closest to 2.4 g/cm3. Zinc is the closest on the Chemistry Reference Table at 2.702 g/cm3. You identify the substance as zinc.
- You would then calculate percent error.
- Percent Error = (Actual amount - experimental amount) x 100
Actual amount
- Percent Error = (2.702 - 2.4) x 100 = 11.2 % error
2.702
Density is the mass of an object relative to its volume. Objects with a lot of matter in a certain volume have a high density, while objects with a small amount of matter in the same volume have a low density.
Floating: Does an orange float on water?
What you'll need:
- An orange
- A deep bowl or container
- Water
Instructions:
- Fill the bowl with water.
- Put the orange in the water and watch what happens.
- Peel the rind from the orange and try the experiment again, what happens this time?
Density, mass and volume
Scientists use “density” to describe how much mass an object packs into a certain volume. Objects with high density have lots of material packed into a small space. Density determines something’s ability to float or sink. If an object has greater density than the liquid it is in, it will sink. If its density is lower than the liquid, it should float
Floating: Does an orange float on water?
What you'll need:
- An orange
- A deep bowl or container
- Water
Instructions:
- Fill the bowl with water.
- Put the orange in the water and watch what happens.
- Peel the rind from the orange and try the experiment again, what happens this time?
It informs about how compact is the mass(heavy or light) and about the buoyancy.
Algunos cuerpos situados en un líquido se hunden, pero otros flotan. Debido a su PESO los cuerpos tienden a sumergirse, pero a su vez los líquidos donde están sumergidos o parcialmente sumergidos ejercen sobre ellos una fuerza vertical y hacia arriba denominada EMPUJE:pushing force. Este fenómeno fue observado por Arquímedes y se conoce como el ARQUÍMEDES P: A body in a liquid suffers a pushing forcé the same as the weight of the liquid that is evicted“.
Si el peso del cuerpo es mayor que el empuje, éste se hunde. Si el peso es igual al empuje, el cuerpo está en equilibrio. Si el peso del cuerpo es menor que el empuje del líquido, éste flota.
If the weight of the body is higher than the pushing force, it sinks.
If the weight is the same as tthe pushing force is on balance.
If the weight is less than the pushing force it floates.
4.1.3. Identifica y explica las principales características de la flotabilidad en un medio líquido.
If the weight of the body is higher than the pushing force, it sinks.
If the weight is the same as than the pushing force is on balance.
If the weight is less than the pushing force, it floats.
Observe the figure:
For a body can float on a liquid it must have less density than the liquid where it floats.
1.Practice: Sink ballons on a bowl. The 1st contains sand, the second contains air and the third contains water.
2.Practice: Pour different liquids on a glass and test which one has got more density and explain it.
Milk, water and oil.
3.Practice: Does the orange float on water?
lunes, 4 de marzo de 2019
Zara and the 1.001 ideas
En inglés vamos apreparar una obra de teatro titulada Zara and the 1001 ideas que en realidad es una adaptación moderna del primer cuento de Las mil y una noches. El texto está en inglés, pero unos narradores la van explicando en español, para facilitar la comprensión del texto. El problema es que tiene 14 papeles, por lo que vamos a dividir el grupo en dos y así todos los alumnos podrán participar.
A ser posible me gustaría representarla en nuestra clase y que cada grupo la representara a otro distinto, es decir, uno a 4º y otro a 5º.
A ser posible me gustaría representarla en nuestra clase y que cada grupo la representara a otro distinto, es decir, uno a 4º y otro a 5º.
domingo, 3 de marzo de 2019
Práctica de informática de 4-3-19.
Materia-Español
Copiaesta direcciónhttp://concurso.cnice.mec.es/cnice2005/93_iniciacion_interactiva_materia/curso/materiales/indice.htm examina las etiquetas y sigue los pasos que se te pidan:
1. Estados,
2. Sólidos,
3. Liquidos,
4. Gases
5. Cambios
6. Actividades finales
Materia-Inglés
Copiaesta direcciónhttp://http://www.physics-chemistry-interactive-flash-animation.com/matter_interactive.htm examina las etiquetas y sigue los pasos que se te pidan:
Suscribirse a:
Entradas (Atom)
